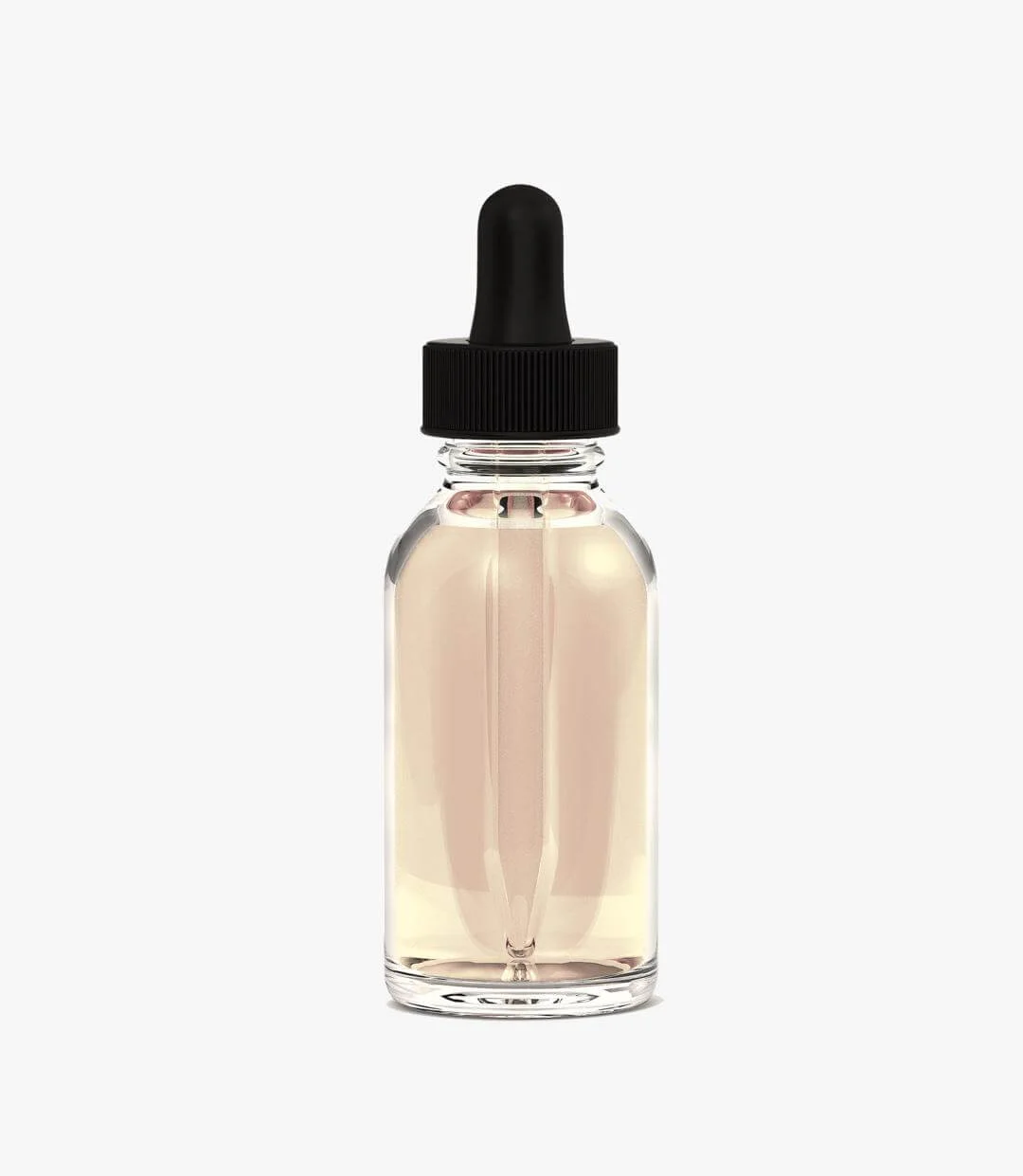
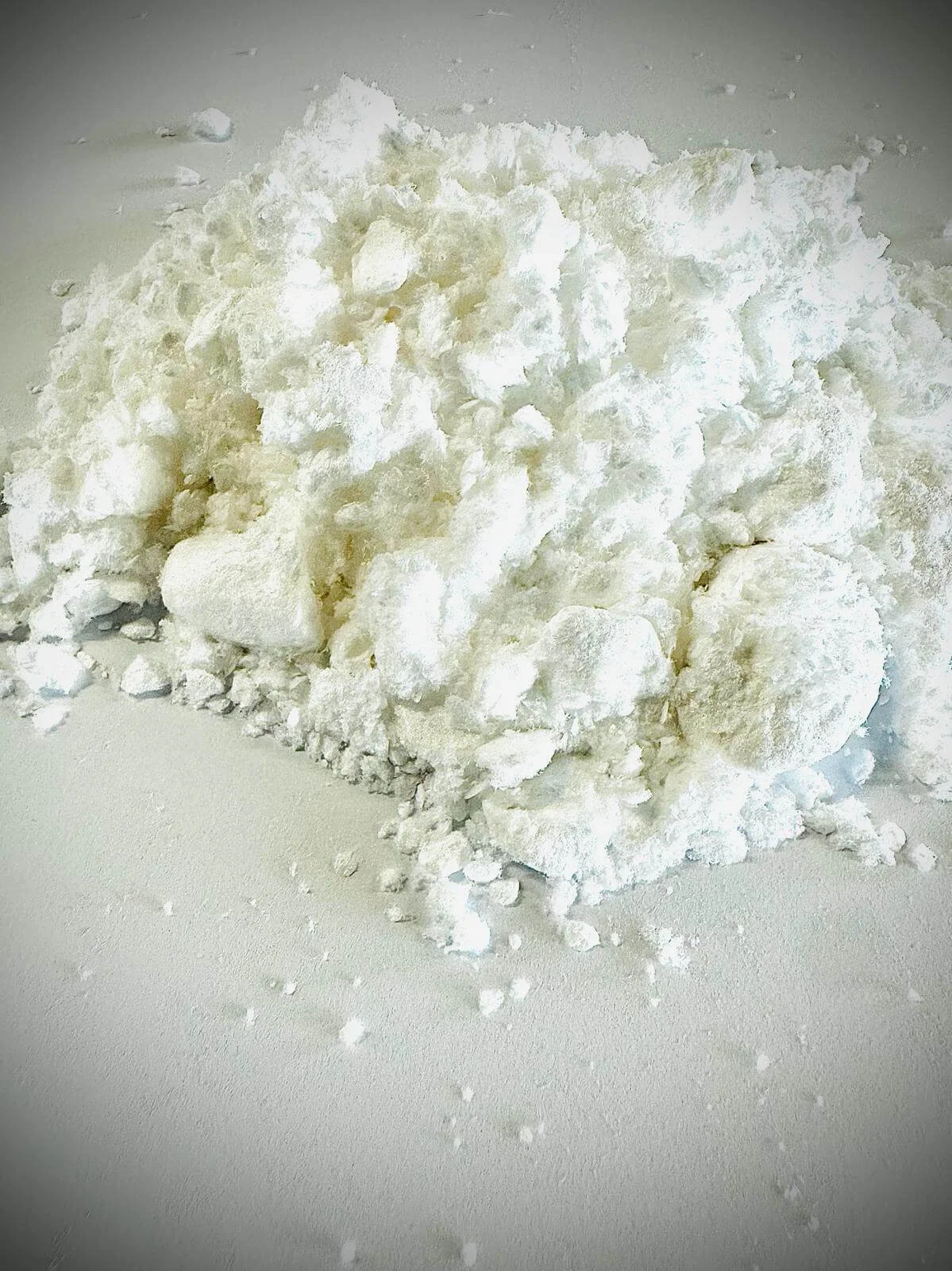
CBG (Cannabigerol) is a rising star in hemp, rivalling CBD as the next non-psychoactive cannabinoid to dominate the low-THC market. Not only does CBG exhibit therapeutic benefits, it’s also unique in that it acts as a chemical precursor to every other cannabinoid in the plant including CBD and THC. As the market begins to understand CBG’s value, the demand is rising.
What are the benefits of CBG?
While CBG-specific studies are still in their infancy, animal studies indicate that CBG may be a neuroprotective agent that also promotes bone health and pain relief, to name a few. CBG has also been shown to exhibit anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, and antibacterial properties, while contributing to bladder and skin regulation. And that’s just the tip of iceberg. More research is needed but CBG shows great potential to treat a wide variety of medical conditions.
How is CBG made?
CBG is extracted through a chromatography process that uses superfluid liquid solvents like CO2 or ethanol to extract the cannabinoid. During the extraction process, hemp is dissolved in the solution, which draws the cannabinoids and terpenes out of the plant. The solution is then evaporated with heat under a vacuum to remove all the gas and leave a high purity CBG concentrate behind. Once extracted, CBG products should be stored at room temperature away from direct sunlight to preserve potency.